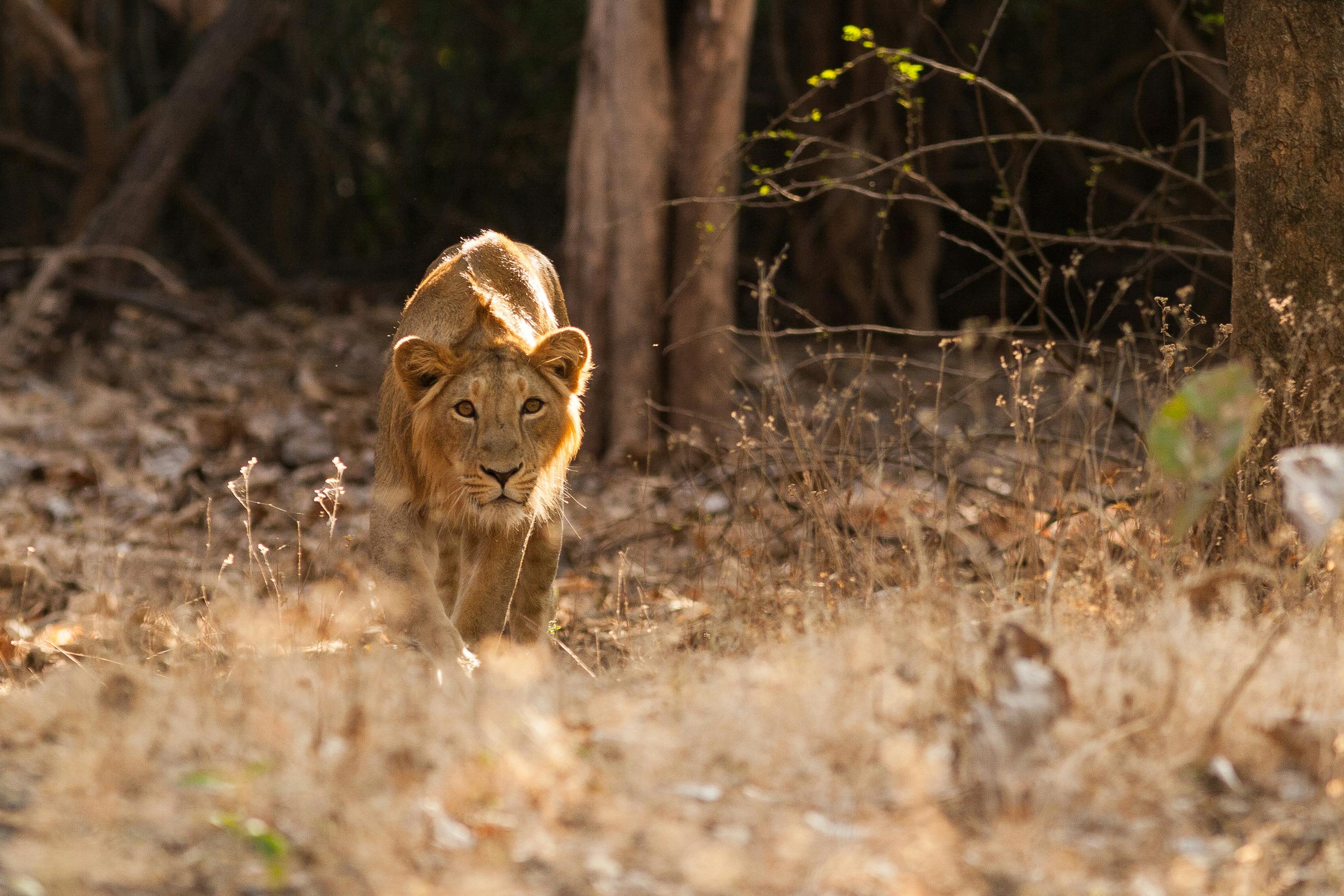
Lions are well known as large, dangerous predators of the African savannah. But did you know that there are lions in Asia too? Once there were many, but today there are fewer than 1,000! To help this feline claw back from near extinction, Rotterdam Zoo coordinates the European population management program for the Asiatic lion. This way, we ensure a reserve population of these impressive predators in zoos, which we keep as healthy as possible with the help of scientific research.
Panthera leo persica

16 - 18 years
90 - 125 centimeters
1.4 - 2.5 meters
♀ 120 - 190 kilograms
♂ 150 - 225 kilograms
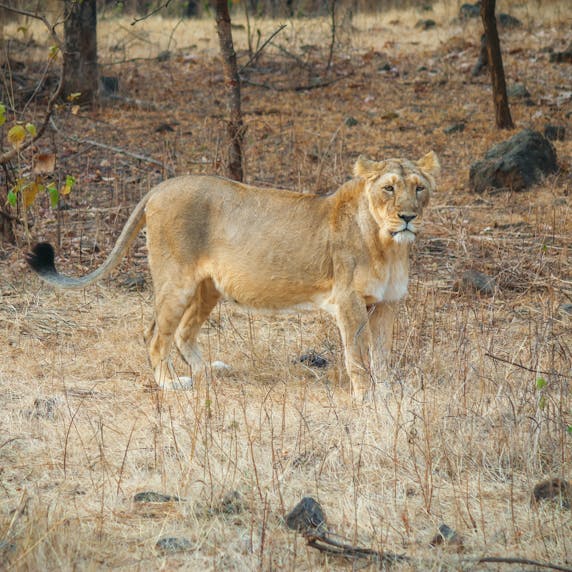
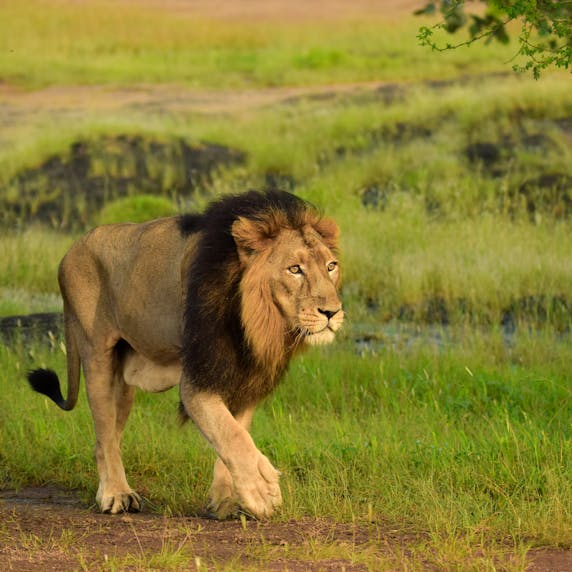
Lions are big cats, recognisable by their muscular build, golden brown coat and long tail with a dark plume at the end. Males also have a thick mane around their neck. Females do not have this.
The difference between Asian and African lions can also be seen in the mane: it is slightly less impressive than that of its African relatives. Asian lions are also generally slightly smaller and have a fold of skin along the length of their lower abdomen.
The Asiatic lion used to be found from Persia (Iran) to eastern India. Nowadays, they can only be found in the Gir Forest National Park in western India. Unlike their African relatives, who hunt on open plains, Asiatic lions live mostly in forests.
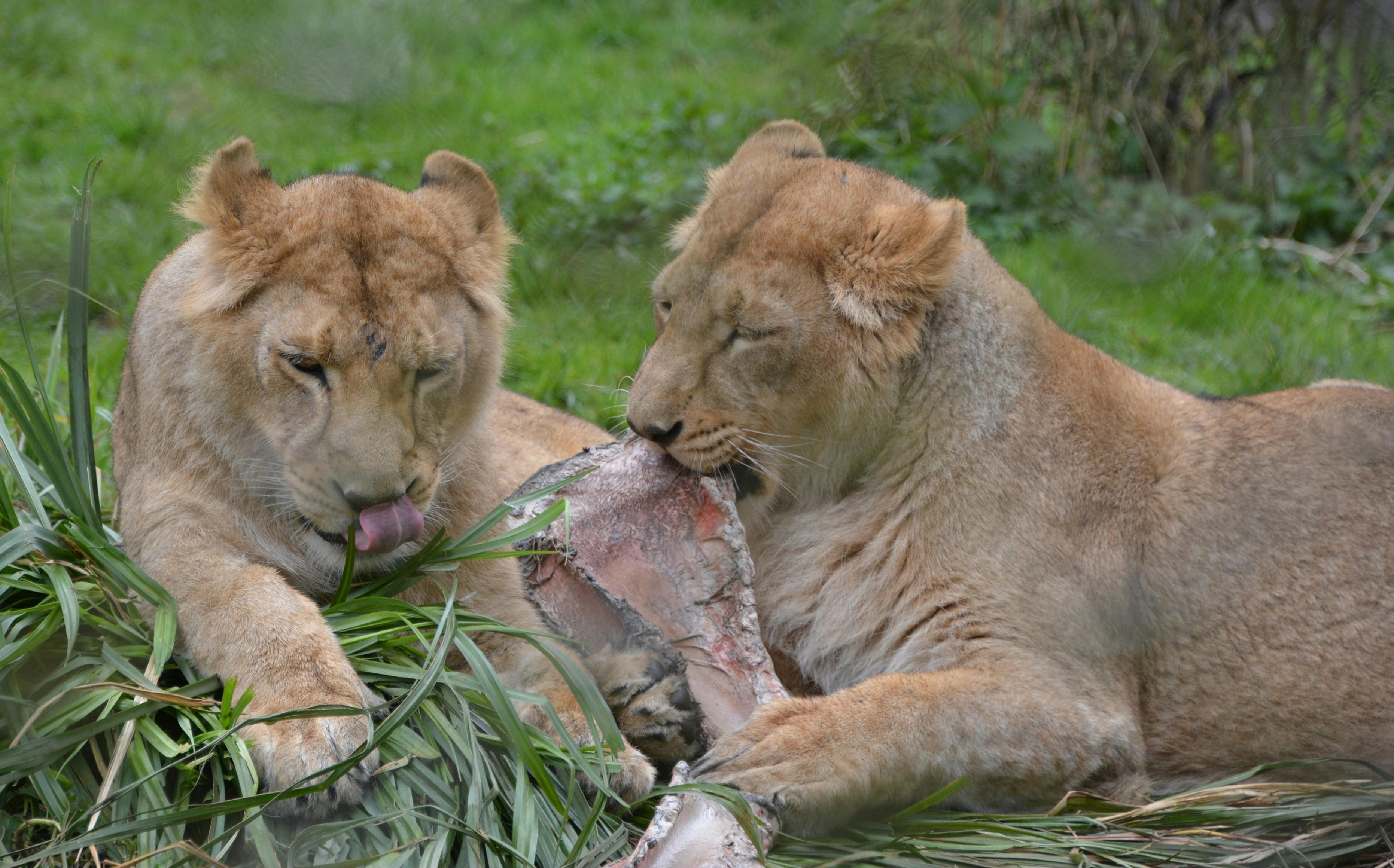

Asiatic lions usually hunt alone. They can hide well in the wooded environment where they live. When an unsuspecting boar, deer or antelope comes too close, the lion pounces to seize its prey.
By hunting these animals, the lion ensures that there are not too many herbivores in the area. This prevents the forest from being stripped bare. That is why large predators such as lions are very important for their habitat.
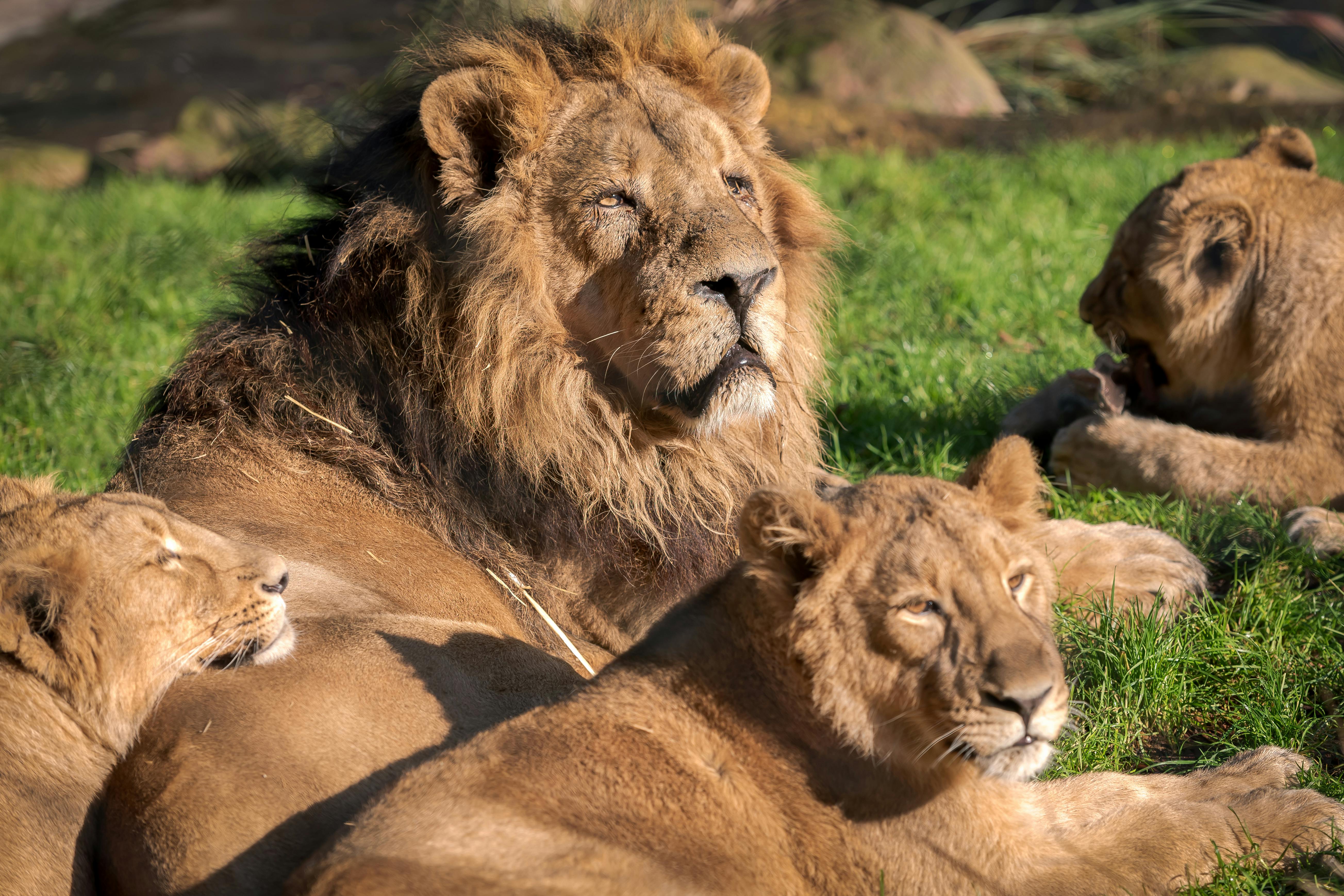

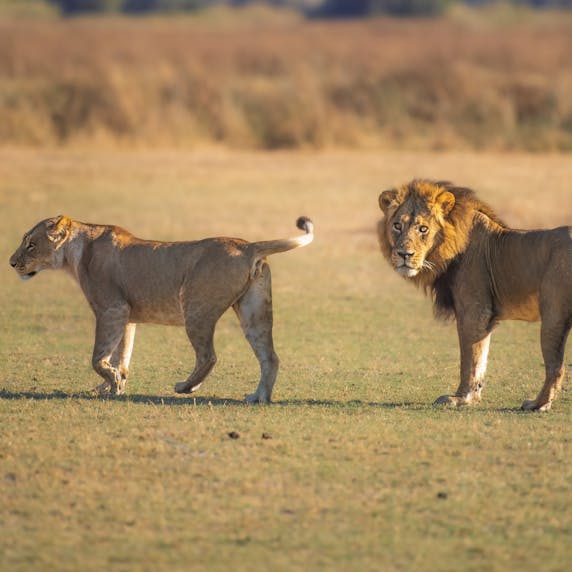
Unlike other cats, which usually live alone, lions are very social animals. Usually, one male guards a group of females and their cubs. Although these “prides” of African lions often consist of 4 to 6 adult females, Asiatic lion prides often only have 2 to 3 females.
Sometimes two or three males team up to guard several groups of females. Together, they have a better chance of warding off wandering males. The social structure of lions is very complex, and scientists are discovering more and more about it.
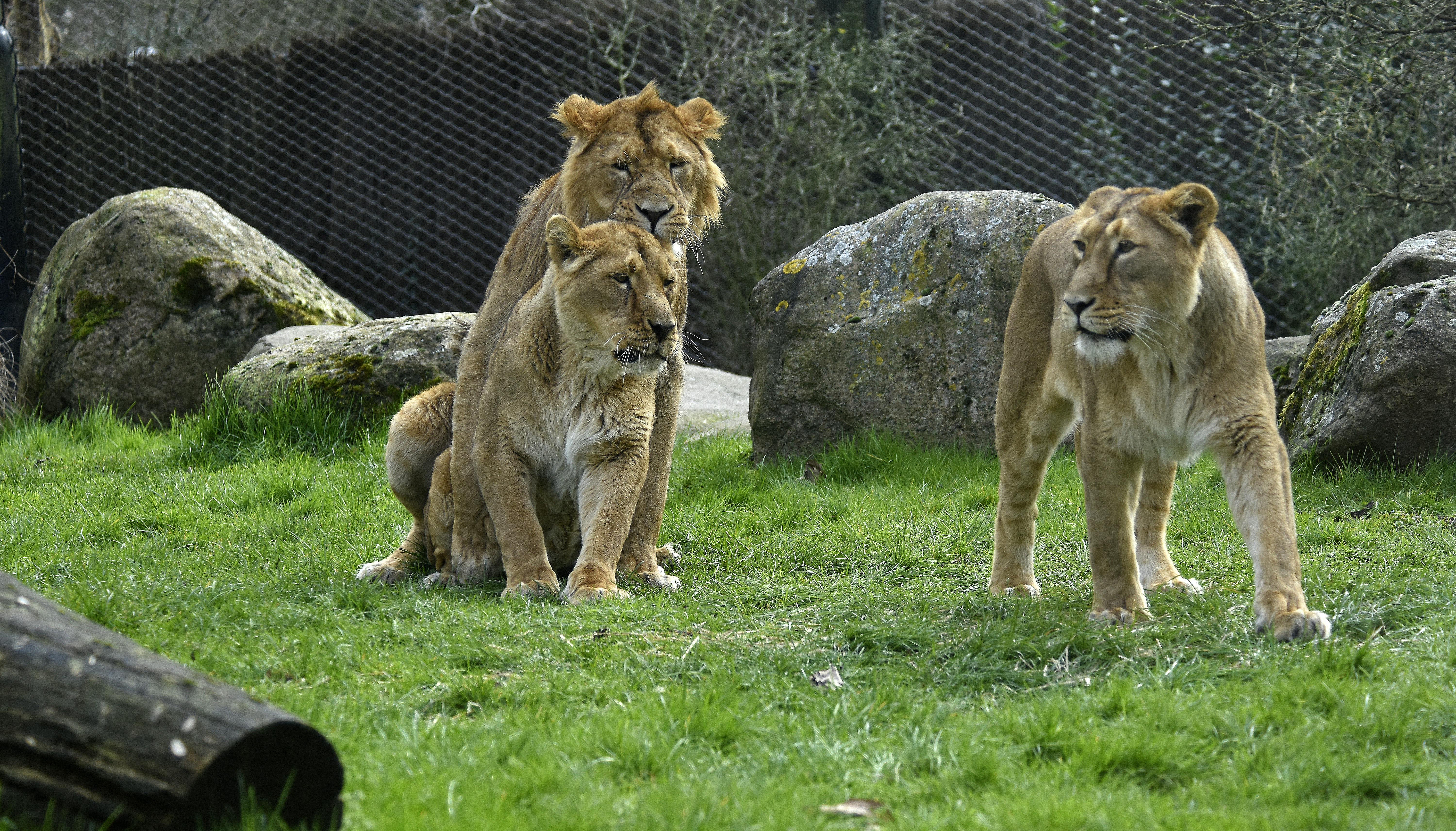

Asiatic lion males guard a number of females, keeping other males away. Lions do not have a fixed mating season: the male must wait until the female is ready.
Sometimes a new male tries to take over the group by chasing away or even killing the old male. If he succeeds, he first kills all the cubs. He does this so that the females are fertile again sooner and he can produce his own offspring. That is why zoos must always be very careful when introducing a new male lion.
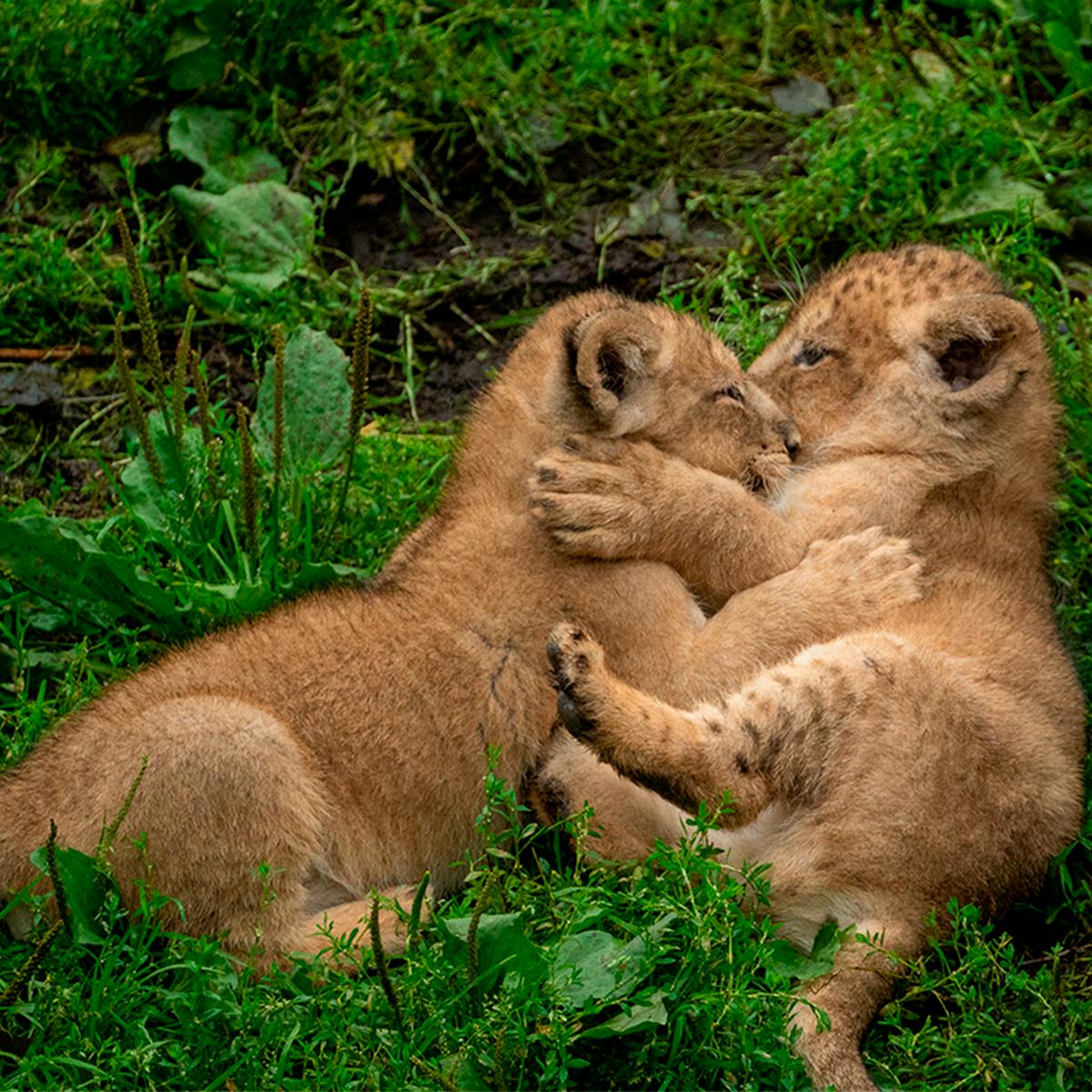

Asiatic lions usually give birth to two or three cubs, which weigh around 1.5 kilograms at birth. The mother first hides in a safe place with her cubs before taking them to the pride. There, the cubs are cared for by all the females: sometimes they even suckle from other lionesses.
Lion cubs learn a lot from each other and their parents. They play to learn how to fight and run. When they are big enough, they watch their parents hunt. This is how they practise important survival skills. After 2 to 3 years, they leave the pride where they were born in search of a new pride.

Asiatic lions are at the top of the food chain. This means that few animals hunt Asiatic lions. However, they do share their habitat with striped hyenas, Indian leopards and wild dogs. These predators all hunt similar prey. Lions therefore sometimes fight to protect or steal carcasses.
Asiatic lions also prefer to stay away from mugger crocodiles and Indian cobras. They used to share their habitat with Asian elephants, Indian rhinos and Bengal tigers, but due to the decline in the habitats of all four species, they no longer encounter them in the wild.
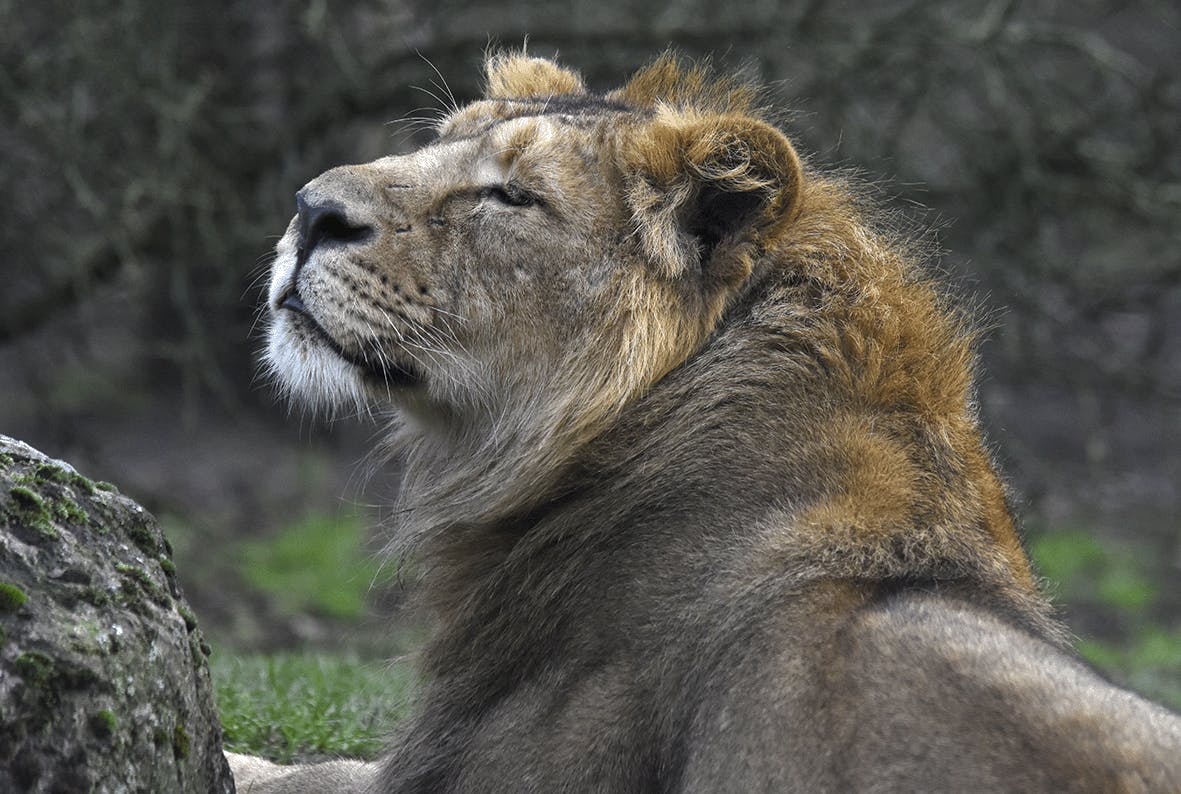

Around 1900, the number of wild Asiatic lions reached an all-time low. At that time, there were fewer than 20 animals left. Since then, hunting lions has been banned and their habitat has been increasingly protected. As a result, the number of lions in India is rising again. In 2017, there were already 650! Although the Asiatic lion is doing better and better, most animals are descended from the same ancestors. This means that the risk of inbreeding among Asiatic lions is quite high. The status of the Asiatic lion in the wild is therefore still “Endangered”.
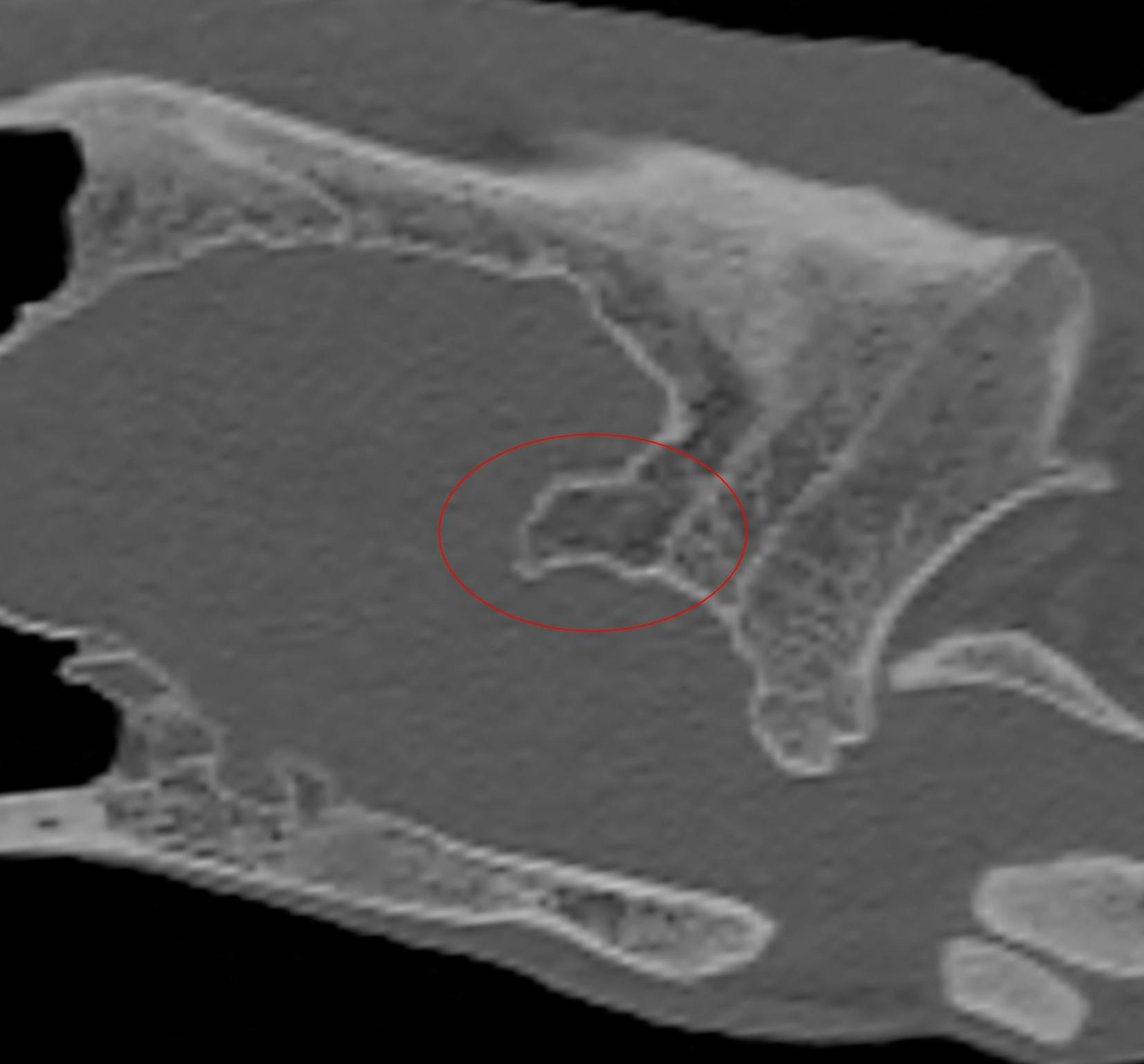
Asiatic lions in zoos often have problems with their balance. They walk unsteadily or sometimes even fall over. These lions have a thickening in their skull, which compresses the brain. The balance problems that this causes are also known as ataxia.
The cause of ataxia is still unknown. It may be hereditary and so common among Asiatic lions because the risk of inbreeding is so high. Another possibility is a lack of vitamin A. We are conducting scientific research to try to uncover the cause of ataxia and find ways to prevent the condition. This will help the lion get back on its feet.
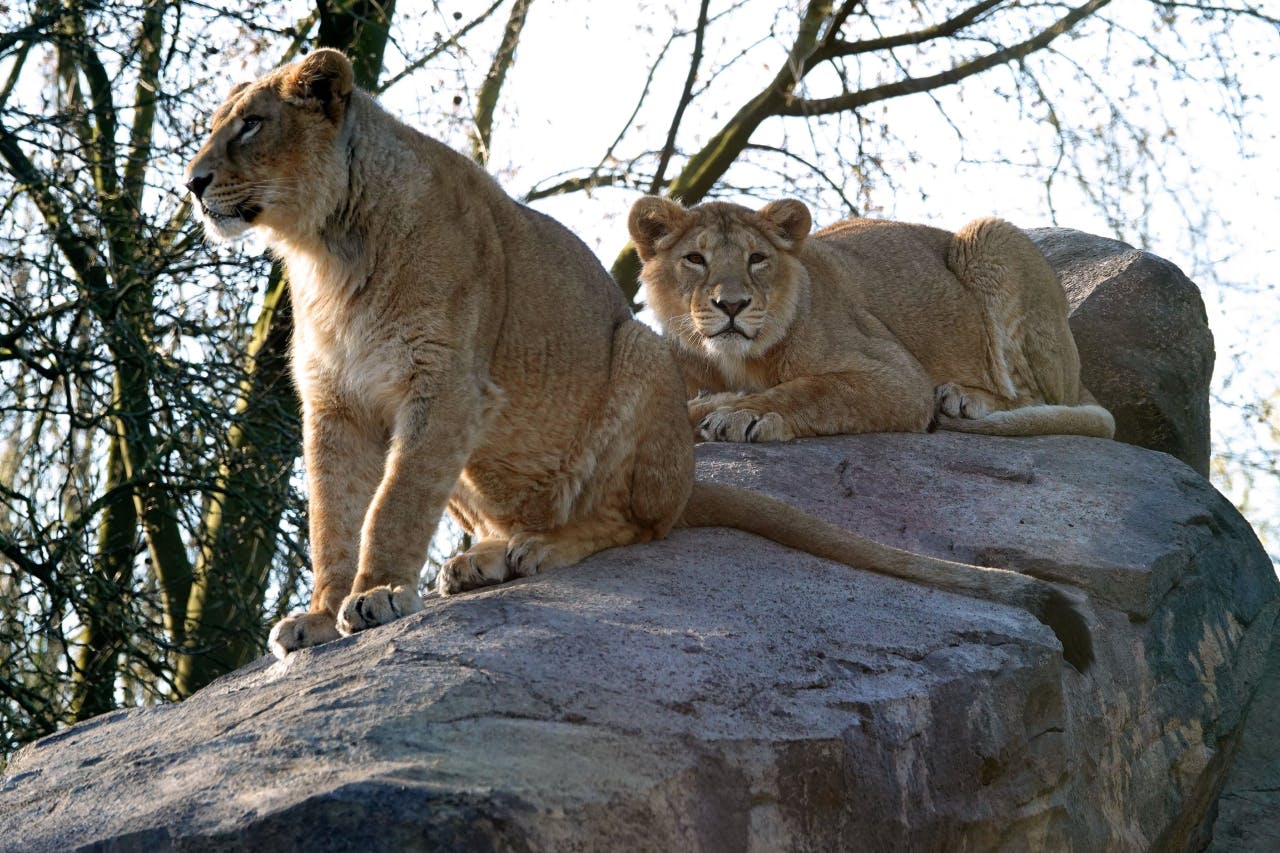

Rotterdam Zoo coordinates the European population management programme for Asiatic lions. Based on the pedigree of lions in zoos, the coordinator determines which animals are best suited to each other for producing healthy offspring. These cubs are then moved to other zoos to form the next generation. In this way, we are building up a healthy population as a reserve for wild animals, with the ultimate goal of returning lions to their natural habitat when conditions are favourable.

For €2.50 you can contribute to a healthy meal for the Asiatic lion.

For €5 you contribute to a better environment for the Asiatic lion.

For €10 you contribute to education about the Asiatic lion.



